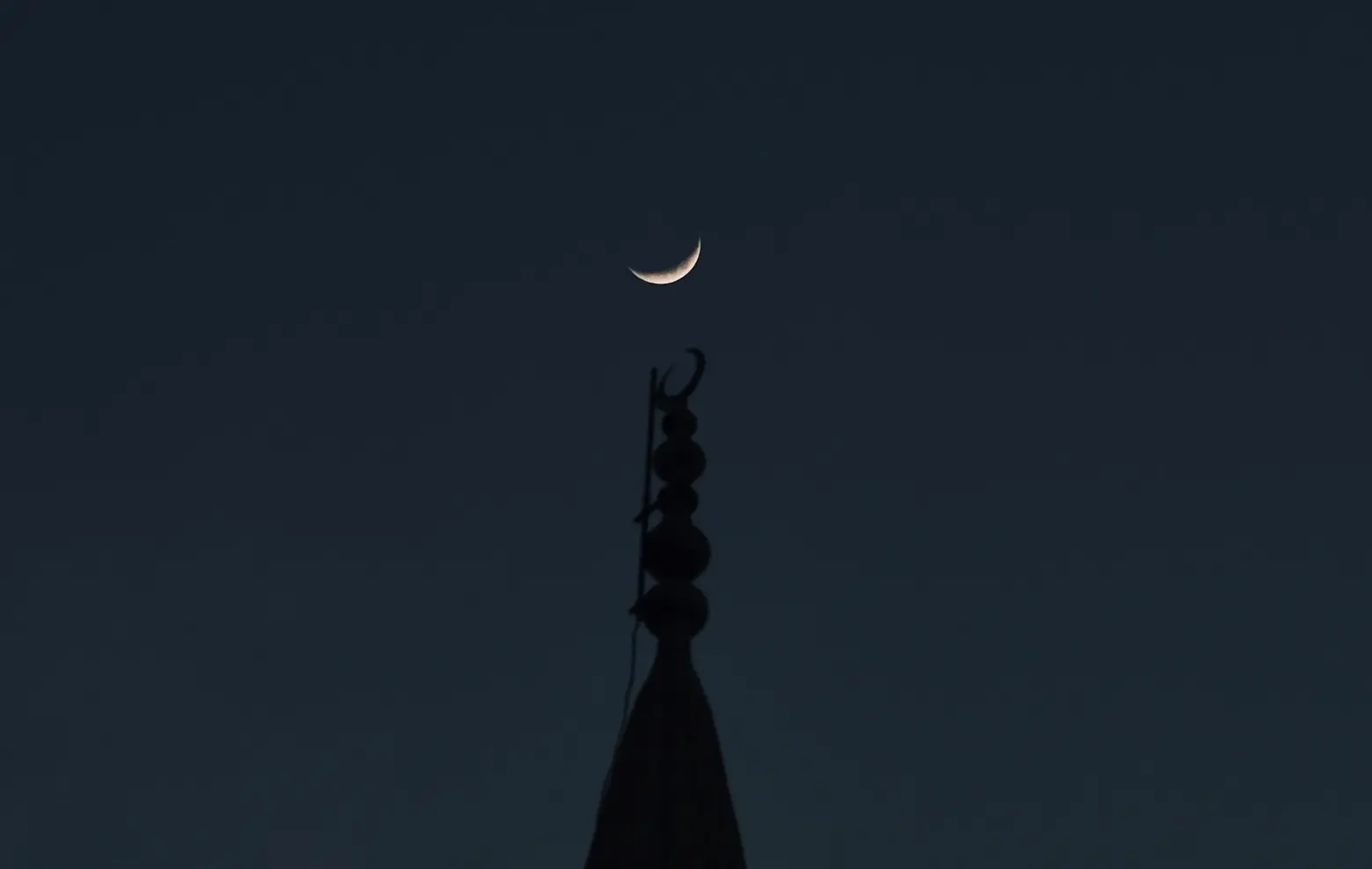
Here is Islamic date today:
[hijri_date]
What is the Islamic Calendar?
The Islamic calendar, or the Hijri calendar, is a lunar calendar consisting of 12 months in a year of 354 or 355 days. It is used to determine the proper days of Islamic holidays and rituals, such as the annual fasting period and the proper time for the pilgrimage to Mecca.
History of the Islamic Calendar
The Islamic calendar was introduced by Caliph Umar ibn Al-Khattab in 638 AD. The starting point of the Islamic calendar is the Hijra, the migration of the Prophet Muhammad and his followers from Mecca to Medina in 622 AD. This event marks the beginning of the Islamic era, and thus, the year 622 AD is considered the first year of the Hijri calendar.
Structure of the Islamic Calendar
The Islamic calendar is purely lunar, meaning that its months begin with the sighting of the new moon. This results in the Islamic year being about 10 to 12 days shorter than the solar year, causing Islamic months to drift each year when compared to the Gregorian calendar.
The months of the Islamic calendar are:
- Muharram
- Safar
- Rabi’ al-awwal
- Rabi’ al-Thani
- Jumada al-awwal
- Jumada al-Thani
- Rajab
- Sha’ban
- Ramadan
- Shawwal
- Dhu al-Qi’dah
- Dhu al-Hijjah
Importance of the Islamic Date and Time
The Islamic date is significant for Muslims around the world as it dictates the observance of various religious duties and festivals. Here are a few key events:
Ramadan
Ramadan, the ninth month of the Islamic calendar, is a holy month of fasting, introspection, and prayer for Muslims. Fasting during Ramadan is one of the Five Pillars of Islam.
Eid al-Fitr
Eid al-Fitr marks the end of Ramadan and is celebrated with communal prayers, feasting, and giving of alms.
Hajj and Eid al-Adha
Hajj, the pilgrimage to Mecca, occurs during Dhu al-Hijjah, the twelfth month. Eid al-Adha, the Festival of Sacrifice, commemorates the willingness of Ibrahim to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to God.
Islamic Time
Islamic timekeeping traditionally starts with the sunset, unlike the Gregorian calendar where the day begins at midnight. This method aligns with the Islamic prayer times, which are determined by the position of the sun.
Five Daily Prayers
Muslims perform five obligatory prayers each day at specific times:
- Fajr: Pre-dawn
- Dhuhr: Midday after the sun passes its zenith
- Asr: Afternoon
- Maghrib: Just after sunset
- Isha: Night
These prayers are spread throughout the day and help Muslims maintain a strong connection with God.
Benefits of Using the Islamic Calendar
Religious Significance
For Muslims, following the Islamic calendar ensures that they observe their religious duties correctly. It also helps them remain connected to their faith and the traditions of the Prophet Muhammad.
Community and Cultural Identity
The Islamic calendar fosters a sense of unity and shared identity among Muslims worldwide. Observing Islamic months and events collectively strengthens the bonds within the Muslim community.
Historical Preservation
The Islamic calendar preserves the historical events of early Islam, such as the Hijra and the battles fought by the Prophet Muhammad, which are integral to Islamic heritage.